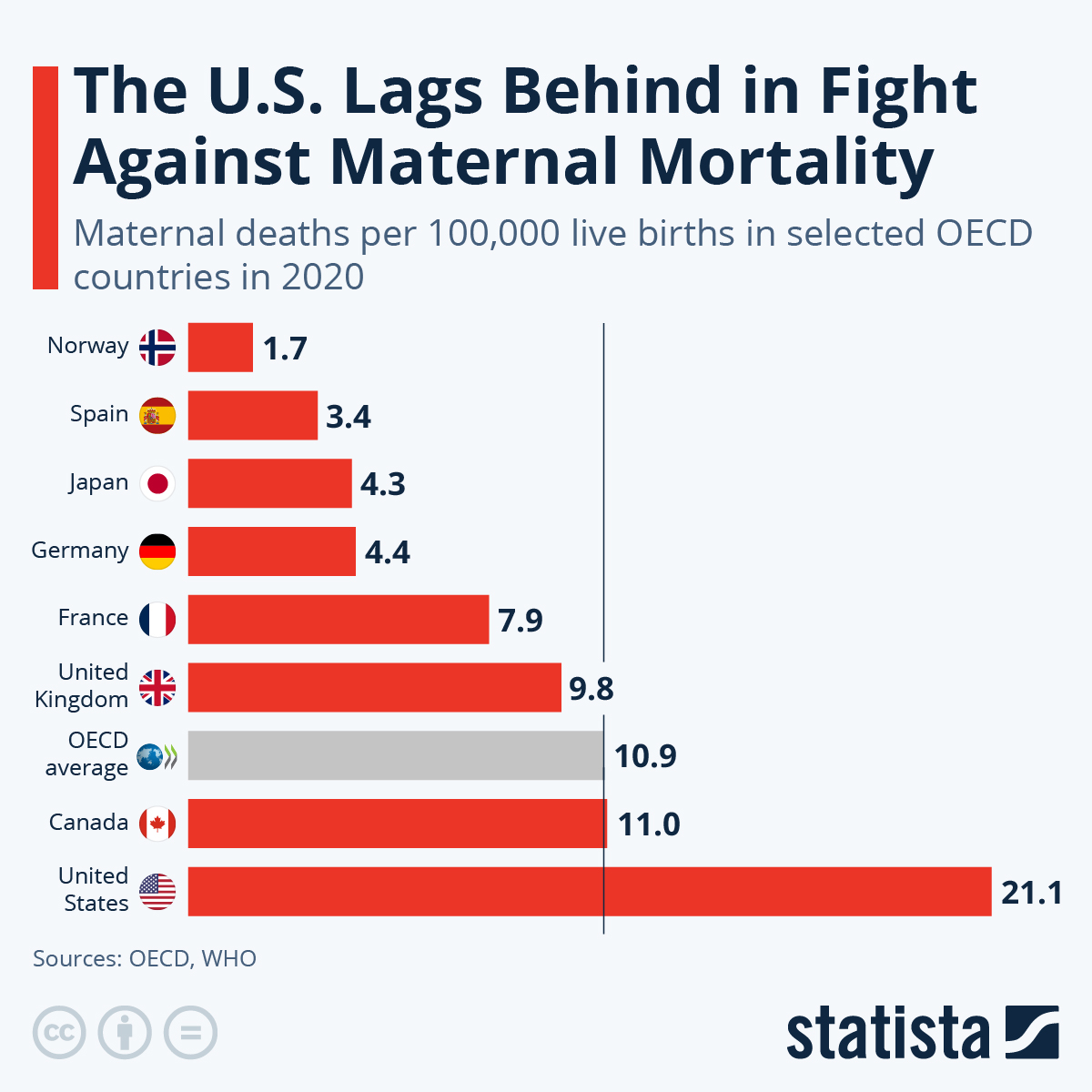
Maternal mortality remains a critical issue in the United States, where pregnancy-related deaths have alarmingly continued to rise, highlighting significant maternal health disparities. This troubling trend underscores the urgent need for improved prenatal care and comprehensive postpartum care policies. While it is estimated that over 80% of these deaths are preventable, systemic inequities and challenges within the healthcare infrastructure exacerbate the situation. The U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, which demand immediate attention to enhance healthcare policies and eliminate disparities among different racial and ethnic groups. Addressing these complexities is vital to ensure safer pregnancies and healthier outcomes for mothers.
The issue of maternal mortality, often referred to in discussions of pregnancy-related deaths, varies widely across geographic and demographic lines, reflecting deep-seated health inequities in society. As we delve into the topic of maternal health, it becomes evident that critical factors such as access to quality care during pregnancy and adequate postpartum support are essential for reducing risks. The alarming trends indicate that without targeted efforts to improve prenatal and postpartum health services, along with effective healthcare policies, mothers remain vulnerable. Understanding the breadth of maternal health disparities is crucial in formulating strategies that promote safety and care for all expectant mothers. A concerted focus on these areas is imperative to reverse the disturbing trajectory of maternal mortality.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
Maternal mortality has become a pressing issue in the United States, where recent statistics reveal a troubling trend: more than 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. This troubling reality contributes to the U.S. having the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. The increase in pregnancy-related deaths has been particularly troubling, as data indicates a significant rise in rates from 2018 to 2022, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. Researchers have found that American Indian and Alaska Native women suffer from the highest mortality rates, almost four times that of white women, which underscores the underlying health disparities that persist across different racial and ethnic groups.
These statistics not only highlight the urgent need for high-quality prenatal care but also emphasize the importance of effective healthcare policies to adequately address these disparities. Policymakers must prioritize maternal health by focusing on the prevention of pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among underserved racial groups.
One of the pivotal findings of recent studies is that cardiovascular disease is now the leading cause of maternal mortality, overtaking hemorrhage. This alarming shift highlights a surge in chronic conditions among pregnant individuals, particularly younger populations who are increasingly affected by hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders. With rising maternal mortality rates, particularly among middle-aged women, it’s crucial that healthcare systems adapt to focus on prenatal care and monitoring chronic illnesses effectively.
Investing in comprehensive maternal healthcare during both pregnancy and the extended postpartum period is essential. This approach can significantly impact maternal health outcomes, reducing preventable deaths and ensuring that all women receive the care they need throughout their motherhood journey.
The Role of Healthcare Policies in Reducing Maternal Mortality
Healthcare policies play a critical role in addressing maternal mortality and improving maternal health outcomes across the United States. The disparities highlighted by recent studies reflect the fact that state-level variations in how maternal care is provided can lead to life-or-death differences for pregnant individuals. Policies that promote equitable access to quality prenatal and postpartum care can help mitigate these disparities significantly. For example, California’s efforts to lower maternal death rates serve as a model for other states, indicating that targeted initiatives can lead to successful outcomes.
Moreover, it’s essential for policymakers to recognize the continuum of care required during pregnancy and postpartum. Traditional practices surrounding maternal care often neglect the full year following childbirth, which is critical for monitoring mothers’ physical and mental health. Legislative measures must reflect an understanding of this continuum, improving access to healthcare resources for women long after delivery. By enhancing healthcare policies that focus on comprehensive maternal health, we can better tackle the alarming rise in preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Impact of Maternal Health Disparities on Communities
Maternal health disparities create significant challenges within communities, particularly among marginalized racial and ethnic groups. These disparities are often interwoven with broader social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, and education. The stark differences in maternal mortality rates, especially among American Indian, Alaska Native, and Black women compared to their white counterparts, illustrate how systemic inequities can jeopardize the well-being of entire communities.
As communities grapple with these disparities, it becomes evident that addressing maternal health cannot be siloed from approaches aimed at overall health equity. Community engagement and tailored public health interventions that resonate with specific demographic needs can foster a healthier environment conducive to reducing maternal health disparities.
Furthermore, investing in community-based initiatives that empower women and encourage them to advocate for their health is crucial. By cultivating supportive networks, educating women about their rights, and ensuring access to quality care, communities can collectively work toward reducing maternal mortality rates. Programs that extend to postpartum support, such as mental health services and chronic disease management, can significantly contribute to healthier maternal outcomes, reinforcing the interconnected nature of maternal health and community wellness.
The Importance of Prenatal Care for Maternal Health
Prenatal care is a foundational element in ensuring healthy pregnancy outcomes and reducing maternal mortality. Early and regular access to prenatal services allows healthcare providers to monitor the health of both the mother and the developing fetus. Regular check-ups during pregnancy can help detect and manage potential complications, such as gestational diabetes and hypertension, both of which can lead to serious outcomes if left unaddressed.
Moreover, comprehensive prenatal care provides education and resources that empower expecting mothers, providing them with knowledge about healthy lifestyle choices, warning signs of complications, and available support services. By prioritizing prenatal care, healthcare systems can target high-risk populations effectively and work toward lowering the high rates of pregnancy-related deaths, ensuring that all women receive essential, timely, and high-quality care.
Additionally, integrating mental health support within prenatal care services recognizes the importance of maternal mental well-being during pregnancy. Addressing both emotional and physical health is vital for reducing the likelihood of postpartum complications and potential maternal mortality. By fostering a holistic approach to prenatal care, healthcare providers can better support women throughout their pregnancy journey, ultimately contributing to improved maternal health outcomes and lower rates of preventable death.
Postpartum Care: An Overlooked Opportunity
Postpartum care is a critical component of maternal health, often overshadowed by the focus on prenatal services. However, as research indicates, nearly a third of maternal deaths occur during the postpartum period, highlighting the need for continued monitoring and support long after childbirth. Effective postpartum care involves not only physical recovery but also addressing mental health challenges that can arise after giving birth, such as postpartum depression or anxiety.
Healthcare policies need to ensure that postpartum care is recognized as an essential part of maternal health. By extending postpartum visits and care to include comprehensive physical and mental health evaluations, healthcare providers can reduce preventable maternal mortality and improve maternal health outcomes significantly. Women’s health should not be treated as if there is a cutoff between pregnancy and motherhood; rather, it is a fluid continuum that needs ongoing attention.
Moreover, better postpartum care involves providing new mothers with access to a range of resources, from nutritional support to education about managing chronic health conditions that may influence their well-being. Ensuring that women receive adequate postpartum healthcare means acknowledging their needs during a vulnerable time—when complications can arise weeks or even months after delivery. By enhancing the focus on postpartum care within healthcare systems, we can make strides in reducing the maternal mortality rate in the U.S., while also promoting the long-term health and well-being of mothers.
Preventing Pregnancy-Related Deaths Through Community Engagement
Community engagement is an essential strategy in preventing pregnancy-related deaths and improving maternal health outcomes. Empowering communities to take active roles in the maternal health discourse fosters awareness of the social and systemic factors contributing to high maternal mortality rates. Grassroots initiatives that focus on educating expectant mothers about available resources, care options, and the importance of seeking timely medical advice can significantly influence maternal health outcomes.
Moreover, involving community leaders and advocates in the conversation helps bridge gaps between healthcare providers and those they serve. By creating culturally responsive health programs that resonate with specific community needs, we can enhance the effectiveness of maternal healthcare interventions and foster a supportive environment for expectant mothers.
Furthermore, community health workers can play a vital role in providing outreach and education within diverse communities, reducing barriers to accessing care. By offering services that connect women to healthcare resources and support systems, these workers can help mitigate the effects of systemic inequality in maternal health. Implementing programs that prioritize community engagement not only improves awareness around maternal health disparities but also encourages active participation from women, leading to better health outcomes for mothers and their children.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Maternal Health Outcomes
The COVID-19 pandemic has had profound repercussions on maternal health, exacerbating existing disparities and highlighting the systemic weaknesses within the American healthcare system. Research indicates that the pandemic may have played a role in the spike in pregnancy-related deaths observed between 2018 and 2022, as many pregnant individuals faced increased health risks and barriers to accessing care during this unprecedented crisis. With healthcare resources stretched thin, prenatal and postpartum care often took a backseat, leading to preventable complications and deaths.
Moreover, the psychological impact of the pandemic on expectant and new mothers cannot be understated. Anxiety, stress, and uncertainty have surged during COVID-19, potentially increasing instances of postpartum mental health challenges. An integrated approach to maternal care that includes mental health support is crucial, especially in times of crisis, to ensure the safety and well-being of both mothers and their babies.
As we continue to navigate the aftereffects of the pandemic, it’s vital to reassess and strengthen our maternal healthcare systems. Policymakers must learn from the disruptions caused by COVID-19 and invest in improving access to healthcare, especially for underserved populations that have been disproportionately impacted. Fostering flexibility in healthcare delivery, such as telehealth options for prenatal and postpartum visits, can help maintain continuity of care for mothers, ensuring they receive the support needed to thrive during and after pregnancy.
Addressing Healthcare Disparities to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
Addressing healthcare disparities is imperative to improve maternal health outcomes and reduce the alarming rates of maternal mortality. Recent studies reveal that significant differences exist across racial and ethnic groups, with women of color facing much higher risks during and after pregnancy. It is critical for healthcare systems to implement policies that specifically target these disparities and ensure that all women, regardless of their background, have equal access to quality healthcare services.
Innovative approaches such as culturally appropriate prenatal and postpartum care can help bridge these gaps, making healthcare more accessible and responsive to the needs of diverse communities. By focusing on comprehensive and equitable care, we can begin to change the narrative around maternal health and work toward significantly reducing preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
Additionally, leveraging community partnerships and engaging with local organizations can facilitate targeted interventions to enhance maternal health. For example, providing education about the importance of prenatal care and available resources to underserved populations can empower women to seek the care they need. Programs that offer support during pregnancy and beyond can make a tangible difference in reversing the trends of maternal mortality, fostering a healthier environment for mothers and their children.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The leading causes of maternal mortality in the U.S. include cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths, as well as complications like hypertension and hemorrhage. Understanding these causes is vital for improving maternal health outcomes.
How does maternal health disparity affect pregnancy-related deaths?
Maternal health disparities significantly contribute to the high rates of pregnancy-related deaths, particularly among racial and ethnic minority groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than white women, highlighting the urgent need for equitable healthcare policies.
What role does prenatal care play in reducing maternal mortality?
Comprehensive prenatal care is essential in reducing maternal mortality rates. It helps identify and manage health issues early, such as hypertension, which can lead to serious complications during pregnancy. Improving access to quality prenatal services is a crucial strategy to prevent preventable deaths.
Why is postpartum care necessary in the context of maternal mortality?
Postpartum care is critical because it addresses health concerns that arise after childbirth. Research indicates that nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occur between 42 days and 1 year postpartum. Acknowledging the importance of this period can enhance support systems for new mothers and ultimately reduce mortality rates.
How can healthcare policies improve maternal health outcomes?
Healthcare policies can improve maternal health outcomes by increasing resource allocation for prenatal and postpartum care, enhancing access to services in underserved areas, and addressing systemic disparities that affect maternal mortality rates among different racial and ethnic groups.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on maternal mortality rates?
The COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp increase in maternal mortality rates, particularly in 2021, due to disruptions in healthcare access and rising chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases among pregnant individuals. This underscores the need for resilient healthcare infrastructure.
What are late maternal deaths and why are they significant?
Late maternal deaths refer to fatalities occurring between 42 days and 1 year after childbirth. They are significant because they indicate ongoing health risks during the postpartum period and highlight the need for improved long-term care and monitoring.
How can public health infrastructure be strengthened to address maternal mortality?
Strengthening public health infrastructure involves investing in data tracking systems for maternal deaths, improving healthcare access, especially in high-risk areas, and providing continued funding for programs aimed at enhancing quality care during pregnancy and postpartum.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, which continued to rise between 2018 and 2022, peaking during the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Preventable Deaths | More than 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable, highlighting the need for better healthcare access. |
| Disparities by Race and State | Significant disparities exist, with American Indian and Alaska Native women facing the highest mortality rate at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related death, accounting for over 20% of deaths. |
| Increasing Concern | Rising pregnancy-related death rates across all age groups necessitate increased attention and resources. |
| Importance of Extended Care | Late maternal deaths, occurring up to a year postpartum, should be included in mortality statistics as they significantly impact women’s health. |
| Investment in Public Health | More resources and innovative solutions are needed to improve maternal care during pregnancy and postpartum. |
Summary
Maternal mortality remains a critical public health issue, with the U.S. experiencing alarmingly high rates compared to other high-income countries. Despite the majority of these deaths being preventable, systemic failures within the healthcare system, marked by significant disparities in care and outcomes, contribute to this ongoing crisis. It is essential to focus on enhancing prenatal and postpartum care, addressing racial inequities, and investing in robust healthcare infrastructure to reduce maternal mortality and improve the health outcomes of mothers across the nation.