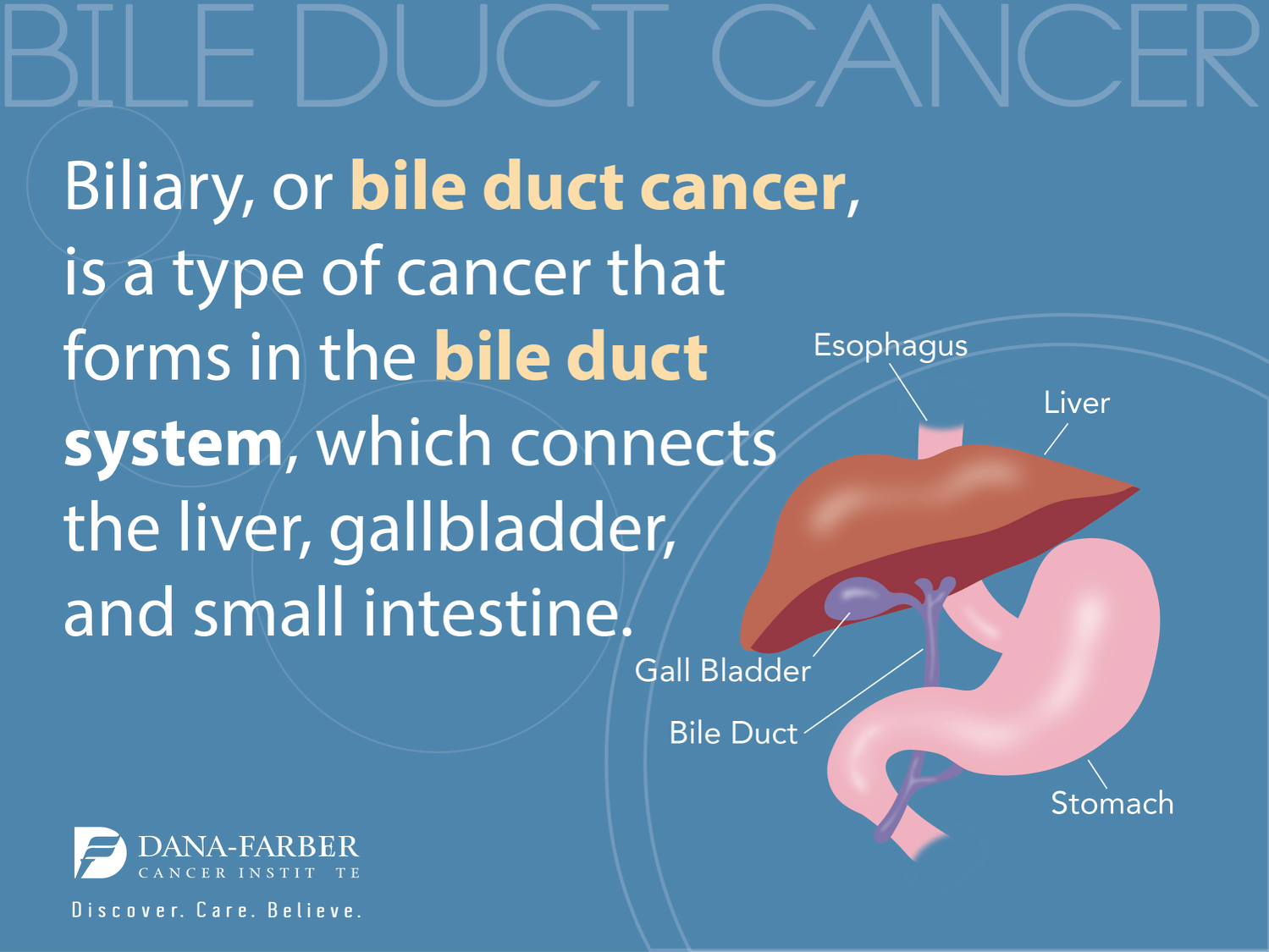
Bile imbalance has emerged as a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the leading form of liver malignancy. Recent studies have highlighted how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can not only promote liver inflammation but also create an environment conducive to cancerous growth. By uncovering key molecular pathways involved in bile regulation, researchers have opened new avenues for potential liver disease treatments. Understanding the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer causes could lead to innovative strategies for prevention and intervention. As we delve deeper into the complexities of liver health, the importance of restoring balance in bile acids becomes increasingly apparent.
The relationship between irregularities in bile composition and liver pathology, notably cancer, is gaining recognition in medical research. Investigating how bile acids influence cellular processes and contribute to disorders such as hepatocellular carcinoma allows for a more nuanced understanding of liver functionality. This exploration encompasses the various hormonal roles that bile acids play beyond their digestive functions, affecting molecular pathways pivotal in cancer progression. By addressing disruptions in bile production and their implications for liver disease management, we can better navigate treatment options and protective measures. Collectively, these insights into bile acid regulation offer promising prospects for the future of hepatology.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism’s Role in Liver Disease
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health and overall metabolic function. Produced in the liver, bile acids not only aid in fat digestion but also participate in regulating cholesterol levels and glucose metabolism. When bile acid production is impaired, it can lead to an imbalance that contributes to various liver diseases, including liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The intricate signaling pathways that control bile acid synthesis and excretion are essential for safeguarding against liver damage.
Dysregulation of bile acids can result in inflammation and cellular injury, creating a perfect storm for liver disease progression. Factors such as genetic predisposition, diet, and environmental influences can exacerbate these imbalances. The significance of understanding these molecular pathways cannot be overstated, as they hold the key to developing targeted liver disease treatments that aim to restore bile acid homeostasis and prevent conditions like HCC.
Linking Bile Imbalance to Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Research has shown a distinct correlation between bile acid imbalance and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As bile duct cells become damaged due to excessive bile acid accumulation, a cascade of inflammation and scar tissue formation ensues. These changes create an environment that is highly conducive to cancer cell proliferation. By mapping out the pathways involved, such as the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, scientists are uncovering how specific molecular switches can either inhibit or promote liver cancer.
One of the critical findings in this area is the role of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), which is essential for maintaining bile acid balance. When YAP functions abnormally, it suppresses FXR activity, leading to an overproduction of bile acids. This disruption catalyzes a series of events that can culminate in the onset of HCC. Thus, therapeutic strategies aimed at modulating YAP or enhancing FXR could potentially reduce the risk of liver cancer development, highlighting the importance of targeting bile acid metabolism in liver disease treatments.
Molecular Pathways in Liver Cancer Treatment
Understanding the molecular pathways involved in liver cancer is imperative for developing effective treatment strategies. The discovery of the Hippo/YAP pathway’s involvement in bile acid metabolism illustrates how cancer progression can be linked to metabolic dysregulation. Interventions that target these specific pathways could lead to innovative treatment options for patients suffering from advanced liver disease or HCC.
Pharmacological approaches aimed at enhancing FXR function or inhibiting the repressive actions of YAP demonstrate considerable promise. Treatments that promote the excretion of bile acids or restore normal acid metabolism could mitigate liver damage and cancer progression. As research continues to unravel the complex relationships between bile acid regulation and liver cancer, the potential for personalized medicine becomes increasingly viable, paving the way for more effective liver disease treatments.
Factors Contributing to Liver Disease Progression
Several factors contribute to the progression of liver disease, with bile acid imbalance as a critical player. Lifestyle choices such as diet, alcohol consumption, and obesity can exacerbate liver conditions. Moreover, the presence of certain genetic markers may predispose individuals to develop hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding these risk factors allows for a multifaceted approach to liver disease prevention and management.
In addition to lifestyle factors, the interaction between various molecular pathways significantly influences liver health. Recognizing the interplay between bile acid regulation and inflammation presents opportunities for therapeutic interventions. By addressing these factors holistically, healthcare providers can devise comprehensive treatment plans aimed at preventing the onset of severe liver conditions, highlighting the importance of early detection and lifestyle modifications.
Emerging Research on Liver Cancer Prevention
Emerging studies shed light on innovative approaches to liver cancer prevention, especially in relation to bile acid metabolism. By exploring the roles of different molecular pathways, researchers can identify key targets for intervention. Modulating these pathways could lead to novel therapeutic strategies that prevent liver injury and inflammation, critical precursors to cancer development.
Moreover, ongoing research aims to refine understanding of how diet and lifestyle modifications can impact bile acid synthesis and liver health. Strategies that enhance bile secretion or optimize digestion may offer straightforward solutions to minimize liver disease risks. Continued investigation into these areas can pave the way for preventive measures that empower individuals to take charge of their liver health.
The Impact of Diet on Bile Acid Production
Diet plays a significant role in the regulation of bile acid production and overall liver health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can support proper bile secretion and minimize the risk of bile acid imbalances. Conversely, diets high in saturated fats and processed foods can disrupt bile acid metabolism, increasing the likelihood of liver disease and potentially leading to conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
Research indicates that specific dietary components can influence the activity of important regulatory proteins like FXR and YAP. Foods that naturally promote bile flow may aid in maintaining a healthy liver environment. Thus, dietary modifications represent a crucial avenue for preventing liver disease and enhancing bile acid homeostasis — an important consideration in the context of liver cancer prevention.
Genetic and Environmental Influences on Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Genetic predispositions significantly influence an individual’s risk for developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Studies have identified several genetic variants associated with impaired bile acid metabolism, which can heighten the likelihood of liver diseases. Alongside genetic factors, environmental influences such as exposure to toxins or viral infections (like hepatitis B and C) can further exacerbate liver damage and influence cancer development.
Understanding the interplay between genetic markers and environmental factors is critical for assessing liver cancer risk. Personalized screening and preventative strategies can be tailored based on an individual’s unique genetic profile, offering a more targeted approach to liver disease management. This genetic insight can lead to proactive interventions that address the underlying risk factors for HCC.
Therapeutic Innovations in Liver Disease Management
The fast-evolving field of liver disease management is witnessing therapeutic innovations driven by insights into bile acid metabolism and molecular pathways. Recent studies have identified promising therapeutic agents that modulate bile acid signaling, offering new hope for patients with liver conditions. For instance, drugs that enhance FXR activity could serve as a basis for new liver cancer treatments, significantly altering the treatment landscape for HCC.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring the potential of combination therapies that not only target bile acid metabolism but also address inflammation and fibrosis. By integrating knowledge of metabolic regulation with advancements in pharmacology, the outlook for liver disease treatment is becoming increasingly optimistic. The goal is to create holistic treatment protocols that improve patient outcomes and diminish the burden of liver cancer.
Future Directions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Research
Future research into hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) will likely continue to focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying bile acid dysregulation and its role in liver cancer. As new technologies emerge, the potential for discovering novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets expands. Ongoing studies will aim to unravel the complex interplay between metabolic pathways, inflammation, and cancer progression, providing invaluable insights for future treatments.
Furthermore, integrating findings from basic research with clinical applications will be crucial. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies will facilitate the translation of basic science discoveries into effective therapeutic strategies. The future of HCC research could lead to breakthroughs that not only improve treatment efficacy but also enhance prevention strategies, ultimately reducing the incidence of liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer causes?
Bile imbalance, particularly in bile acid metabolism, can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruptions in bile acid regulation may cause liver injury and inflammation, setting the stage for cancer development.
How does bile acid metabolism influence the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in liver health. An imbalance leads to excessive bile acid production, which can promote inflammation and fibrosis, ultimately contributing to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through pathways involving molecular switches like YAP and FXR.
What are the potential liver disease treatments linked to bile acid regulation?
Treatments targeting bile acid regulation are promising for liver diseases. Research suggests that enhancing the function of the Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) or promoting bile acid excretion could mitigate liver damage and slow the progression of liver cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
What role do molecular pathways in cancer play in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
Molecular pathways, particularly the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway, play a pivotal role in regulating bile acid metabolism. Disruption of this pathway can lead to bile acid imbalance, contributing to liver injury and the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma.
Can bile acid imbalance lead to inflammation and liver cancer?
Yes, bile acid imbalance can cause inflammation in the liver. Chronic inflammation from excessive bile acids is a significant risk factor for developing liver cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma, by promoting cellular changes that favor tumor formation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | Imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The study highlights the relationship between bile imbalance and cancer progression. |
| Key Molecular Switch | A molecular switch that regulates bile acids has been identified, offering new insights into liver cancer treatment. |
| Role of YAP | YAP was discovered to inhibit FXR, a critical bile acid sensor, leading to excessive bile acid accumulation and liver damage. |
| Potential Treatments | Blocking YAP’s effects or enhancing FXR function may halt liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Implications | Findings could lead to pharmacological solutions targeting FXR to prevent liver cancer. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are intricately linked as new research indicates that disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The identification of YAP’s role in bile acid metabolism provides exciting potential pathways for innovative treatments aimed at preventing liver cancer development. Enhancing the function of bile acid sensors or modifying YAP’s effects could represent groundbreaking approaches in combating liver diseases.