Bile imbalance is increasingly recognized as a significant factor in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of this deadly disease. Recent advances in liver disease research highlight how disruptions in bile acid regulation can lead to liver injury and inflammation, setting the stage for cancer development. By exploring the YAP FXR pathway, researchers have uncovered a critical molecular switch that not only regulates bile acid levels but also presents a potential target for innovative liver cancer treatment. With the revelation that YAP can inhibit the function of a key bile acid receptor, healthcare professionals are gaining new insights into the intricate connection between bile acids and liver health. As the research unfolds, it opens doors to novel therapeutic strategies aimed at correcting bile imbalance and thwarting liver cancer progression.
Elevating our understanding of bile composition and liver malignancies reveals a compelling link between bile acid dysregulation and the onset of liver malignancies such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This emerging body of research underscores the pivotal role of bile acids, not merely as digestive agents but as critical players in metabolic signaling processes within the liver. Furthermore, the identification of molecular pathways, specifically the YAP FXR pathway, paves the way for targeted interventions that could transform liver cancer treatment. Researchers are fervently investigating how alterations in bile metabolism within the liver may contribute to pathologies, opening the dialogue on the importance of maintaining a healthy bile equilibrium. As these insights evolve, they promise to enhance our approach to treating liver cancer and improving patient outcomes.
Understanding Bile Imbalance: Its Role in Liver Disease
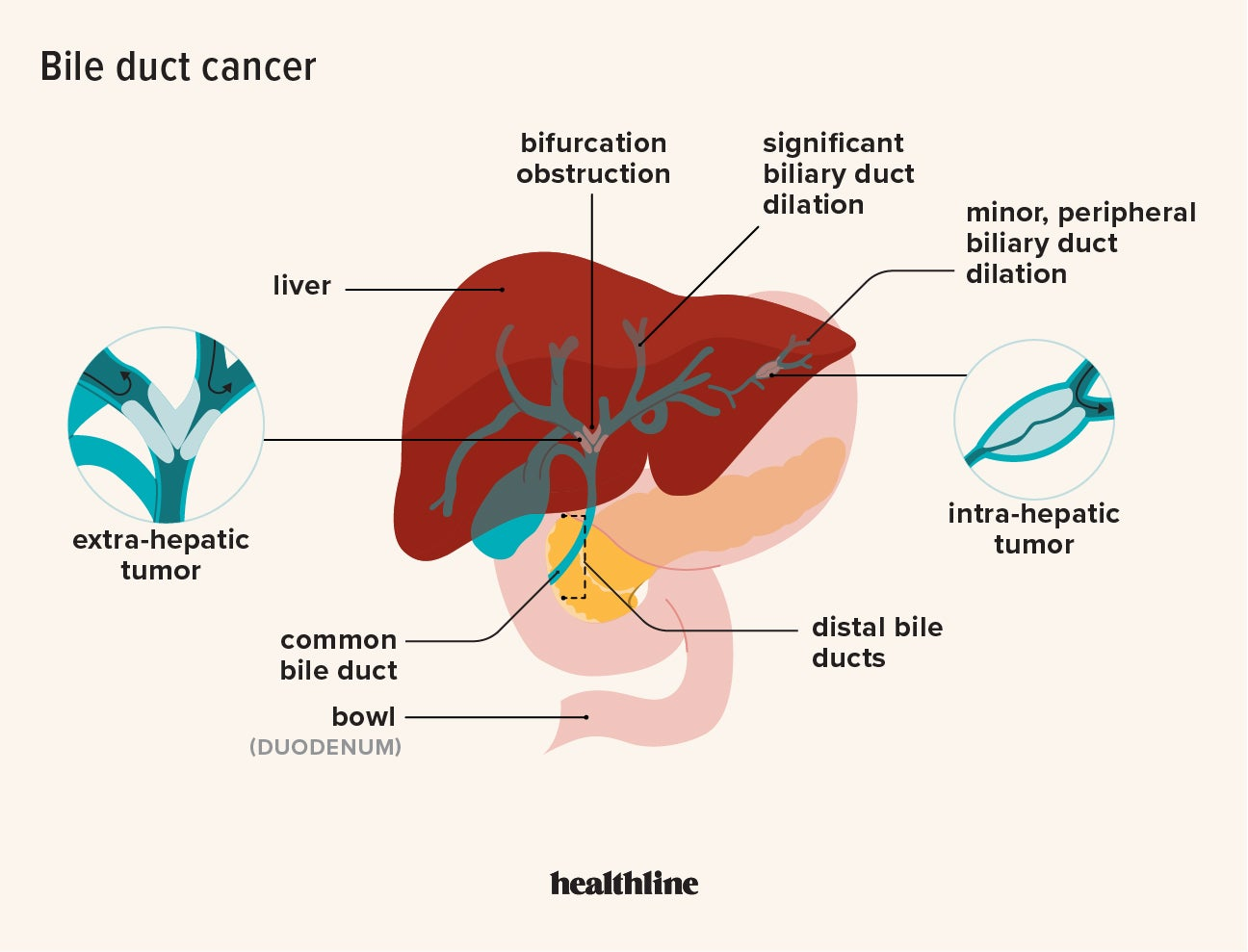
Bile imbalance, a crucial factor in liver health, can significantly impact the development of various liver diseases. The liver produces bile, a digestive fluid comprising bile acids, bilirubin, cholesterol, and electrolytes, essential for fat digestion and absorption. However, when the delicate balance of bile acids is disrupted, it can lead to liver injuries, inflammation, and eventually conditions like hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Researchers have identified that accumulated bile acids can cause cellular stress and activate inflammatory pathways, worsening liver conditions and increasing cancer risk.
Moreover, disruptions in bile acid metabolism can signify underlying liver dysfunction. Studies indicate that elevated bile acid levels can serve as biomarkers for liver disease progression. Understanding this link is crucial as it opens avenues for innovative treatments targeting bile acid pathways. By restoring the normal bile acid balance, it may be possible to mitigate liver damage and reduce the risk of cancer development, emphasizing the need for continued liver disease research focused on this vital area.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile imbalance, particularly the overproduction of bile acids, has been linked to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. Disruption of bile acid regulation can lead to liver injury and increased inflammation, culminating in cancer development.
How do bile acids contribute to liver cancer treatment?
Bile acids play a critical role in metabolic processes, and their imbalance can trigger liver diseases. Understanding bile acid homeostasis and the role of the FXR receptor in regulating bile acid production offers new insights into potential liver cancer treatments, including pharmacological solutions to enhance FXR function.
What is the YAP FXR pathway and its relevance to bile imbalance and liver cancer?
The YAP FXR pathway involves the YAP protein, which regulates bile acid metabolism. In liver cancer, YAP can act as a repressor of FXR, leading to bile acid accumulation and liver damage. Targeting this pathway may provide new therapeutic strategies for managing liver cancer.
What are the implications of bile acid research in liver disease?
Research on bile acids informs our understanding of liver diseases by revealing how bile imbalance contributes to inflammation and cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. Findings from this research may lead to innovative liver cancer treatments that target bile acid metabolism.
How do researchers study the effects of bile acids on liver cancer progression?
Researchers examine bile acids’ role in liver cancer by investigating molecular pathways like the Hippo/YAP pathway, analyzing how bile acid homeostasis is disrupted and its implications for diseases like HCC. These studies utilize molecular, cellular, and genomic methods to understand the link between bile imbalance and cancer.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Health Risks: A critical imbalance in bile acids can lead to liver diseases and is linked to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The liver produces bile to aid fat digestion, but disruption can trigger inflammation and cancer. |
| Research Findings: A molecular switch regulating bile acids was identified. Activation of YAP disrupts FXR signaling, leading to bile acid overproduction and liver damage. |
| Implications for Treatment: Enhancing FXR function, inhibiting YAP, or increasing bile acid excretion could prevent liver damage and cancer progression according to the research findings. |
| Future Directions: The study opens the door for pharmacological approaches to stimulate FXR and improve liver health. |
Summary
Bile imbalance and liver cancer are intricately connected, as recent studies have shown that disruptions in bile acid metabolism contribute significantly to the development of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind bile regulation provides promising avenues for targeted therapies that could mitigate the risks of liver cancer, underlining the importance of maintaining bile acid homeostasis in liver health.