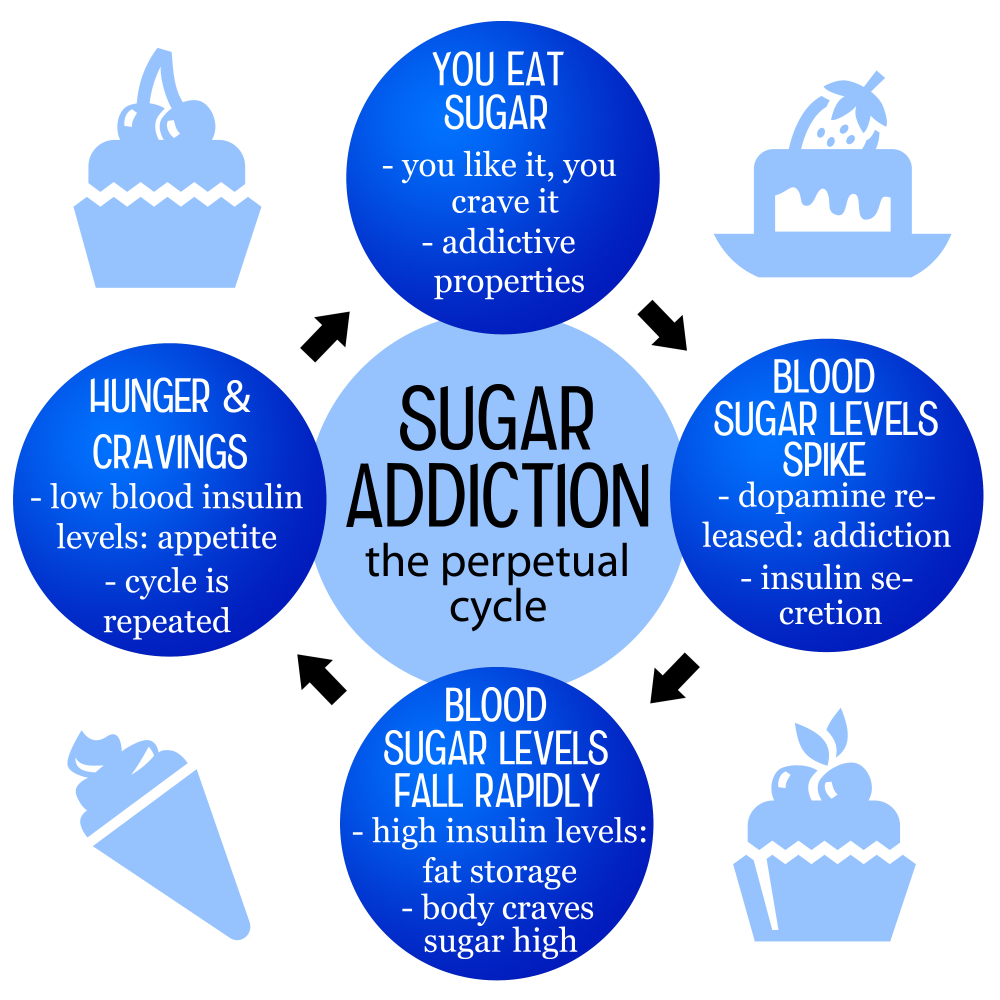
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked intense debate among nutritionists and health researchers alike, as the effects of sugar on our bodies can resemble those of more commonly recognized addictive substances. The phenomenon of sugar addiction, marked by overwhelming cravings and compulsive consumption, raises concerns about the health effects of sugar, especially in a society inundated with processed foods high in added sugars. Current sugar consumption guidelines suggest that we monitor our intake to avoid health issues linked to excessive sugar, such as obesity and diabetes. Understanding the intricacies of sugar-related cravings can empower us to make healthier choices and ultimately navigate our relationship with sweets more consciously.
When discussing the potential addictive nature of sugar, we might also refer to it as a sweet dependency or the allure of sugary treats. This discourse often intertwines with terms like refined carbohydrates and irresistible desserts, which dominate our diets through easy access in sugary snacks and beverages. Many individuals find themselves grappling with a strong desire for these products, as they not only satisfy tastebuds but also trigger neurochemical responses similar to those seen in more intense addictions. As we delve deeper into the impact of these sweet substances on our daily lives, it becomes crucial to explore how the pervasive presence of sugar influences health outcomes and dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction: Is Sugar Really Addictive?
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked significant debate among nutritionists and health experts alike. While substances such as alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on clinical criteria, sugar’s addictive potential is less clear. Research shows that consumption of sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, which resemble addiction in some respects. For instance, the enjoyment that sugary foods provide may trigger the brain’s reward system similarly to addictive drugs. However, it’s important to note that sugar itself is not classified as an addictive substance due to the differences in the withdrawal symptoms experienced when sugar is reduced compared to drugs and alcohol.
Critically, the nature of sugar consumption is intertwined with various food sources, including fruits and vegetables, which are essential for a balanced diet. This complicates the classification of sugar as an addictive substance. Moreover, the average American consumes about 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding the American Heart Association’s recommendations of no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. To mitigate sugar cravings without completely eliminating it, experts recommend gradually reducing sugar intake rather than quitting ‘cold turkey,’ as abrupt changes can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like drugs or alcohol?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive by clinical standards. Unlike drugs and alcohol, sugar is necessary for survival, found naturally in many foods, which distinguishes its effects on the brain from those of true addictive substances.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to several health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The compulsive cravings for sugary, ultra-processed foods often result in excessive sugar consumption, which may contribute to these serious health effects.
What are the symptoms of sugar cravings or withdrawal?
Symptoms of sugar cravings can include intense cravings for sugary snacks, headaches, dizziness, anxiety, and irritability when sugar intake is suddenly reduced. These withdrawal-like symptoms can occur as the body adjusts to lower sugar consumption levels.
What are the recommended sugar consumption guidelines?
The American Heart Association recommends that men limit their added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day, women to 6 teaspoons, and children to even lesser amounts. Being aware of sugar content in processed foods is essential for maintaining healthy consumption levels.
How do processed foods contribute to sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high amounts of added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, making them highly palatable and easy to overconsume. This can create habitual cravings and lead to increased sugar consumption, fostering a cycle that resembles addictive behaviors.
Can reducing sugar consumption improve health?
Yes, reducing sugar consumption can improve overall health by lowering the risk of chronic diseases, enhancing mood stabilization, and decreasing cravings. Gradually cutting back on added sugars can help mitigate withdrawal symptoms and promote healthier eating habits.
What should I do to manage sugar cravings?
To manage sugar cravings, consider gradually reducing your added sugar intake instead of eliminating it entirely. Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods and be mindful of food labels to better monitor your sugar consumption.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Is sugar classified as addictive? | No, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, but it can trigger cravings and compulsive behaviors. |
| Cravings and withdrawal symptoms | People may experience withdrawal-like symptoms (e.g., headaches, anxiety) when they stop consuming sugar-rich foods but these are less severe than those associated with true addictive substances. |
| Need for sugar | Sugar is present in essential foods like fruits and whole grains, making total elimination impractical and unhealthy. |
| Recommended intake | The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even less for children. |
| Gradual reduction | It’s advised to reduce sugar intake gradually instead of going cold turkey to avoid backlash. |
| Importance of moderation | A moderate amount of sugar can enhance food flavor and should not be equated with harmful addictive substances. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate surrounding sugar’s addictive qualities continues in nutritional research. While it does produce cravings akin to addictive substances like alcohol and nicotine, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria to be classified as one. It’s essential to recognize that sugar is a natural component of many healthy foods, and the challenge lies in moderation rather than elimination. Most health experts agree that understanding and managing sugar intake is crucial for overall well-being, as excessive consumption can lead to adverse health effects. Therefore, being informed about sugar content in diets is vital for making healthier choices.